What is Lead?
Lead is a toxic metal historically added to paint and other products to improve product durability, moisture resistance, and color vibrancy. While widely used in the past, lead paint is now recognized as a neurotoxin that is highly hazardous to health, particularly for children and pregnant women.
When was Lead Banned?
Lead-based paint was banned for residential use in the United States in 1978 by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC).
The ban was implemented to address the health risks, especially to children, associated with exposure to lead paint. However, buildings constructed before 1978 may still contain lead paint, posing a potential hazard as the paint deteriorates. When lead paint deteriorates, it can release lead dust or chips, which are easily ingested or inhaled. Lead poisoning can result in serious health problems, including developmental delays, learning difficulties, behavioral issues, and organ damage.

Why is Lead Dangerous?
Lead is hazardous to both adults and children, but children are more vulnerable to its harmful effects due to their developing bodies and brains.
For Adults
- Lead poisoning can result in high blood pressure, kidney damage, and nervous system issues.
- It may cause reproductive problems, such as reduced fertility in both men and women.
- Prolonged exposure at high levels can lead to memory loss, joint pain, and muscle weakness.
For Pregnant Women
Expectant mothers are particularly at risk, as lead can pass from the mother to the fetus, potentially causing premature birth, low birth weight, and developmental problems for the baby.
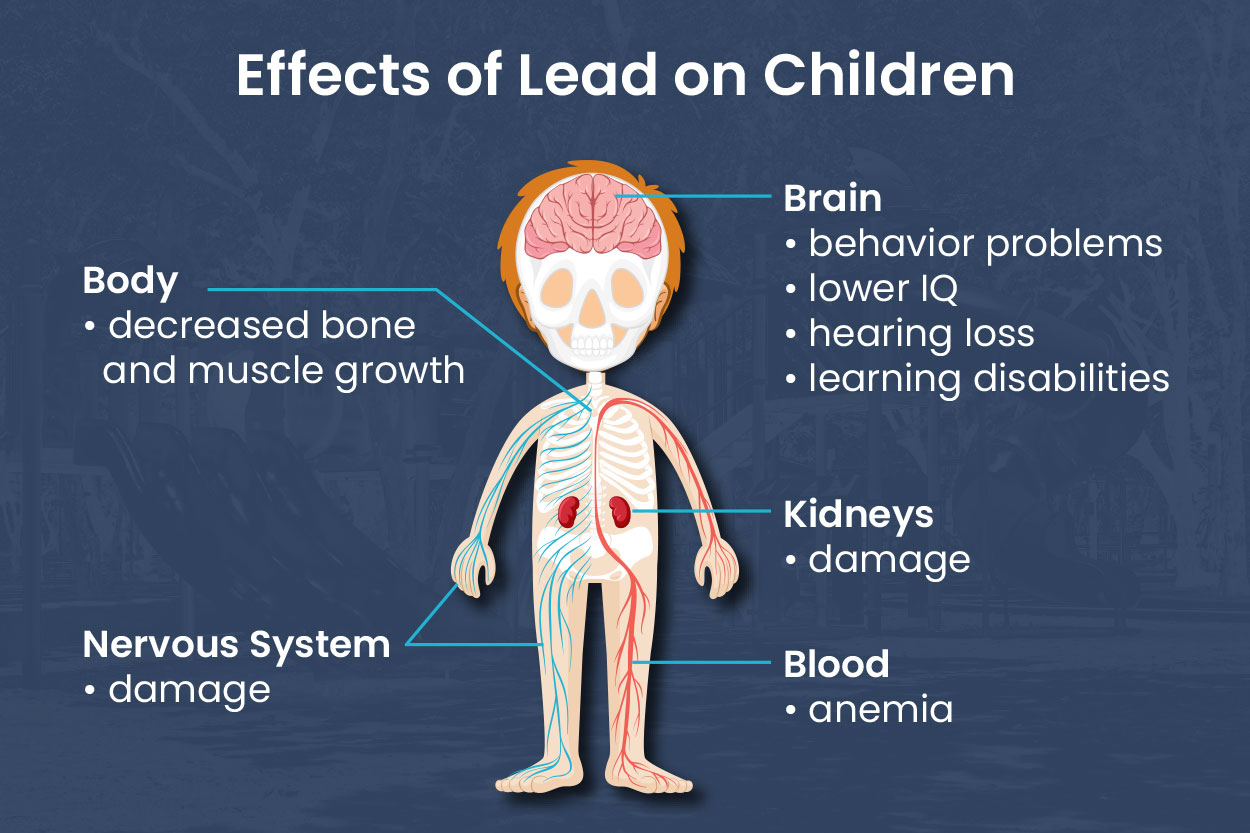
For Children
- Lead exposure can cause developmental delays, learning disabilities, and reduced IQ.
- It may lead to behavioral issues, such as increased aggression or difficulty concentrating.
- Long-term exposure can affect physical growth and cause anemia or hearing problems.
What do I do if I my child or I have been exposed to lead?
Talk to your pediatrician, general physician, or local health agency about what you can do. Your doctor can do a simple blood test to check you or your child for lead exposure. You may also want to test your home for sources of lead.
Lead Paint and My House
Many houses in Cleveland were built before 1978, they may still have lead paint.
What is my landlord required to do?
In 2019 Cleveland City Council passed legislation that requires owners of rental property in the City to prove that their dwelling units are safe from lead hazards.
This proof is a Lead Safe Certification or proof of full abatement of all lead hazards.
As the owner of a rental unit in the City of Cleveland, you are responsible for ensuring your property is free from lead hazards and applying for a Lead Safe Certification.
Rental properties built before 1978 must obtain a Lead Safe Certification or an Exemption. Owner-occupied properties do not need to be certified.
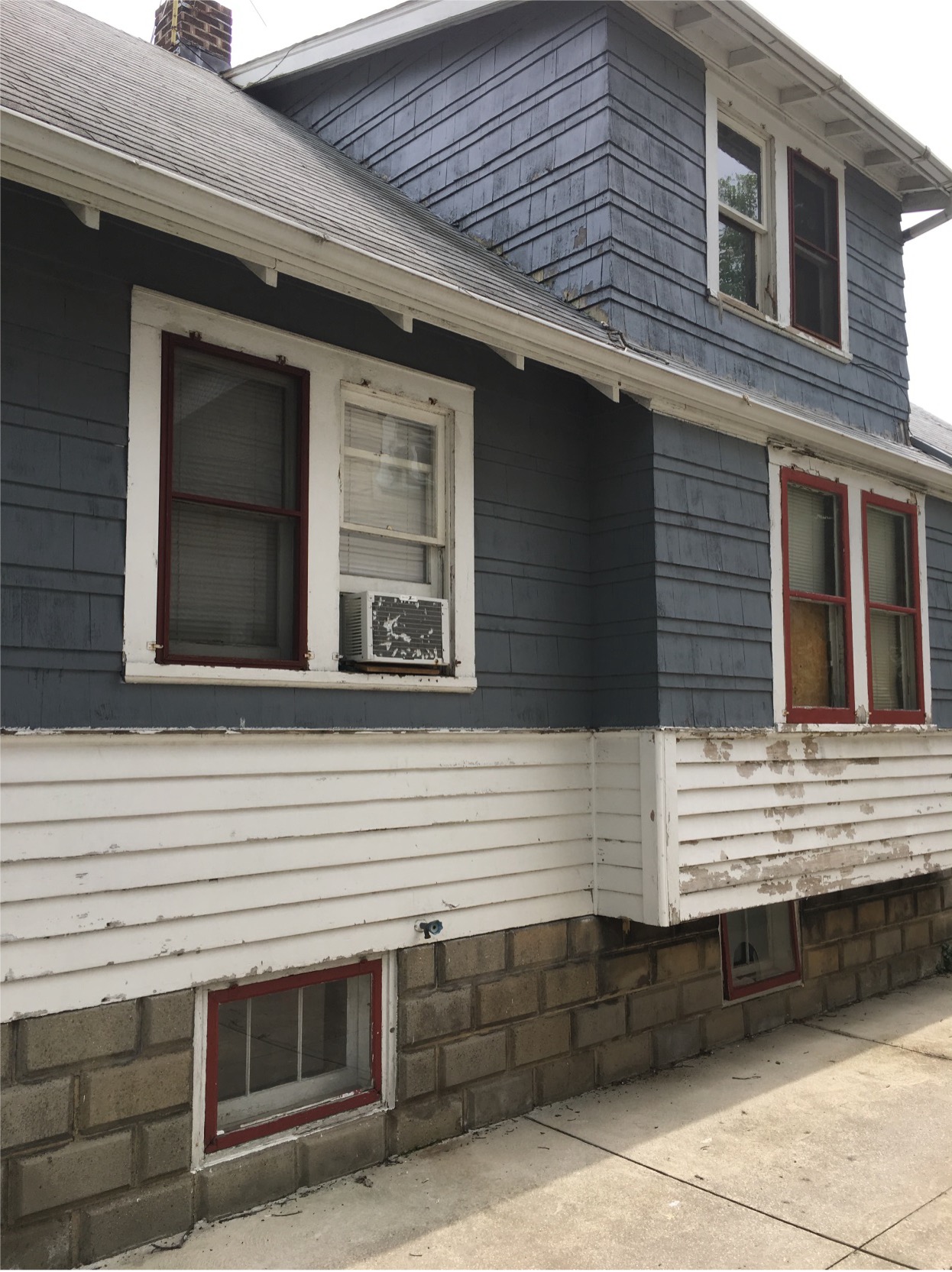
Could there be lead paint in my house?
Lead-based paint was banned for residential use in the United States in 1978 by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC). Buildings constructed before 1978 may still contain lead paint, posing a potential hazard if the paint deteriorates.
Many houses in Cleveland were built before 1978, they may still have lead paint.
Houses that were built after 1978 do not contain lead paint and are exempt from the City's Lead Safe Certificate law.
Where is lead paint in my house?
Check older painted surfaces, especially windows, doors, walls, and railings, and porches.
Uncovered soil poses a risk of lead poisoning and should be covered with mulch or plant material.
Often the drip line around a home’s foundation has exposed bare soil.
How can I check for Lead Risk Assessment on my house?
If the rental unit that you are living in was built prior to 1978, the owner or property manager is required to demonstrate that the unit is lead-safe. You can check on the legal status and any lead warnings about the unit you are living in by accessing the City of Cleveland’s Open Data Portal: Lead Safe Certificates.
You will be able to search by address to determine whether the unit:
- Is certified as Lead-Safe
- Has an assessment describing the work that needs to be done to become lead-safe and the source of any lead hazards on the property
- Is subject to the Lead Safe law, but has not complied
How can I reduce my exposure to lead?
Keep Surfaces Clean: Regularly clean floors, windowsills, and other surfaces with a wet cloth or mop to reduce lead dust. Use a HEPA vacuum.
Avoid Chipping Paint: Do not scrape or sand painted surfaces unless done by a certified lead professional, as this releases lead dust.
Wash Hands and Toys: Encourage frequent handwashing, especially for children, and clean toys regularly.
Lead Poisoning Prevention: Cleaning Your Home
Learn More
Have a question?
For questions regarding the process of obtaining your Lead Safe Certificate, contact:
- Phone: 216.664.2274
- Email: LeadCertCLE@Clevelandohio.gov




